-
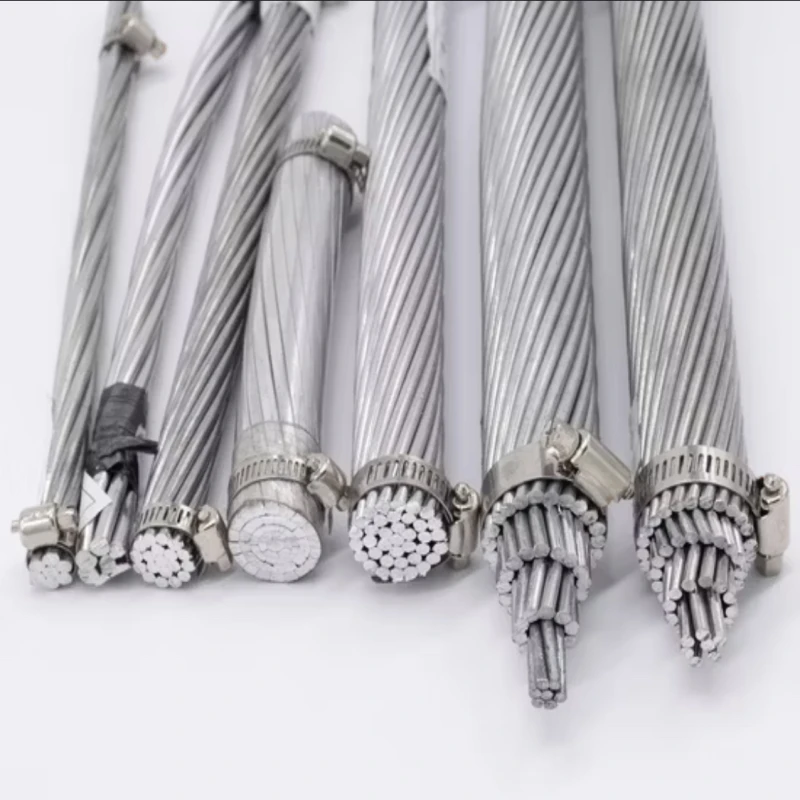
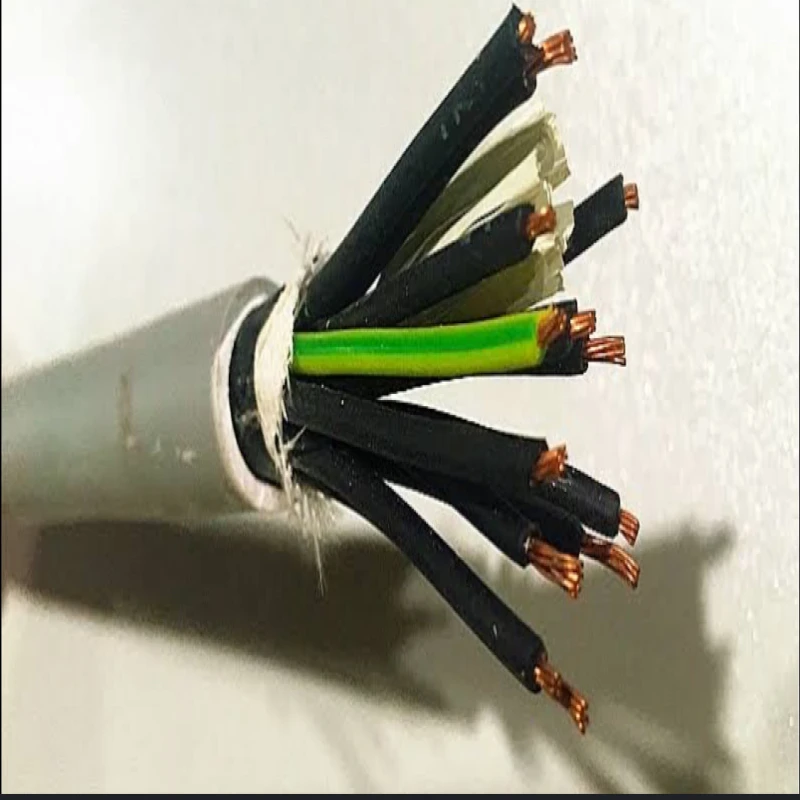
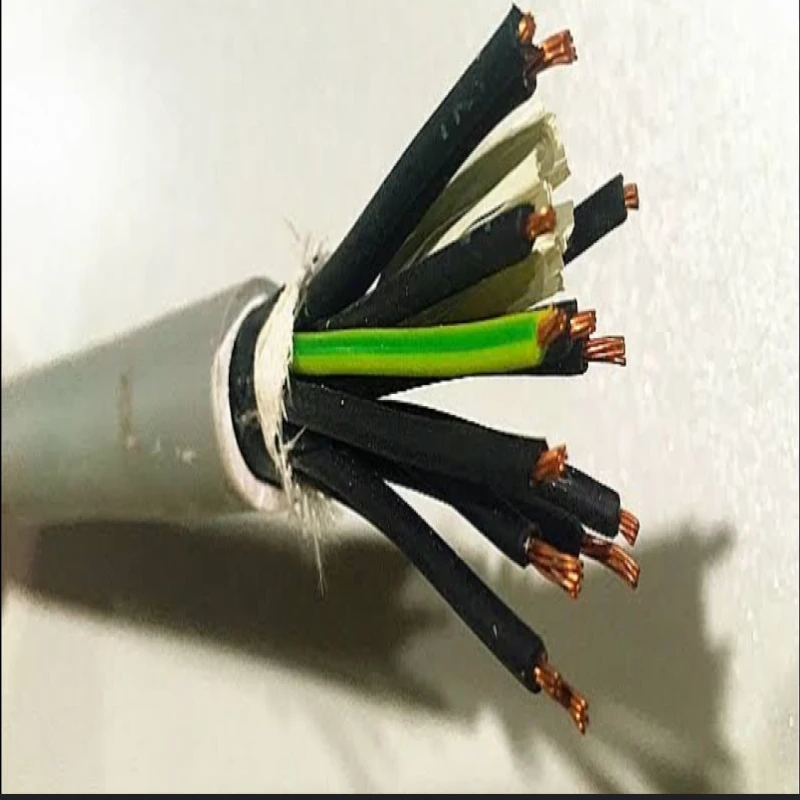
The core of the cable is made of stranded copper (or sometimes aluminum) with a cross-sectional area of 2.5mm².
-
Each core is individually insulated with a material like PVC or XLPE (Cross-linked polyethylene), providing electrical isolation between the conductors.
-
The entire assembly of 12 cores is then enclosed in an outer sheath, often made of PVC, which provides mechanical protection and environmental resistance.
-
Some control cables may include an armour layer, typically steel wire (SWA), for added mechanical protection, especially for underground or harsh environments.
-
These cables are widely used in control systems, automation, and instrumentation applications where multiple signals or power circuits need to be managed simultaneously.
-
The multi-core design allows for efficient transmission of various signals, and the 2.5mm² conductor size provides adequate current-carrying capacity for many control applications.

 APPLIANCES
APPLIANCES ELECTRIC AND POWER
ELECTRIC AND POWER ELECTRONICS
ELECTRONICS FOOD
FOOD GADGETS
GADGETS KITCHEN
KITCHEN SOLAR SOLUTIONS
SOLAR SOLUTIONS